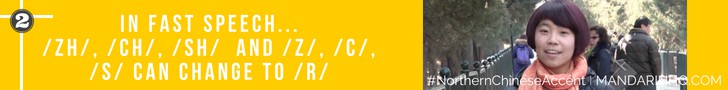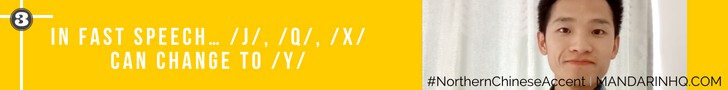In everyday English, “Mandarin” refers to Standard Mandarin.
(The official language of Mainland China and Taiwan)
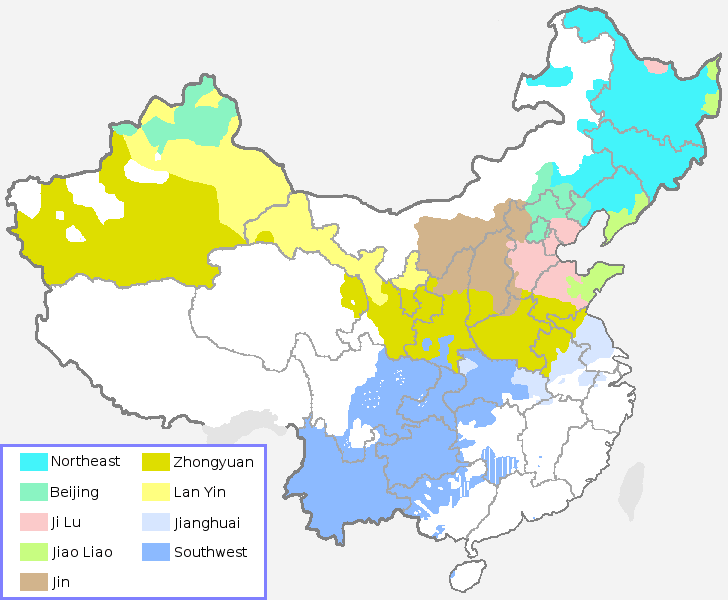
But Mandarin is also a group of related dialects, spoken mostly in northern China.
Mandarin Dialects — a.k.a. “The Northern dialects” 北方话; běifānghuà
Now, as you may know…
Standard Mandarin is based on the Beijing Mandarin Dialect.
And this leads some learners to expect that the average Beijinger — or native speaker of a related dialect — speaks Standard Mandarin without an accent!
So, does reality meet expectation..? (Press play)
BONUS: DOWNLOAD A SUMMARY (MP3 + PDF) BELOW THIS VIDEO
Features of "Northern Accented" Chinese (from the video)
Extensive use of Erhua (儿化)
Erhua is the addition of an "-r" sound at the end of a syllable. (e.g. hua > huar)
This occurs in Standard Mandarin, but it's much more extensively used in casual northern-accented Mandarin.
Examples:
Without Erhua | With Erhua |
|---|---|
dòng huà piān 动画片 Cartoon | dòng huà piānr 动画片儿 Cartoon |
dǒng shì de 懂事的 Sensible | dǒng shìr de 懂事儿的 Sensible |
zán zhè méi dì tiě. 咱这没地铁。 We don't have subway here. | zán zhèr méi dì tiě. 咱这儿没地铁。 We don't have subway here. |
chī wán fàn, qù shàng bān. 吃完饭,去上班。 Finish eating and go to work. | chī wán fàn, qù shàng bānr. 吃完饭,去上班儿。 Finish eating and go to work. |
In fast speech... /zh/, /ch/, /sh/ and /z/, /c/, /s/ can change to /r/
Examples:
Standard Mandarin Chinese | Fast Northern Chinese Accent |
|---|---|
sì shí duō suì. 四十多岁。 40+ years old. tā sì shí duō suì. 她四十多岁。 She's 40+ years old. | sì rí duō suì. 四十多岁。 40+ years old. tā sì rí duō suì. 她四十多岁。 She's 40+ years old. |
bù zhī dào. 不知道。 (I) don't know. wǒ bù zhī dào tā shì nǎr rén 我不知道她是哪儿人。 I don't know where she comes from. | bù rī dào. 不知道。 (I) don't know. wǒ bù rī dào tā shì nǎr rén 我不知道她是哪儿人。 I don't know where she comes from. |
duō shǎo qián? 多少钱? How much? zhèr duō shǎo qián? 这儿多少钱? How much is this? | duō rǎo qián? 多少钱? How much? zhèr duō rǎo qián? 这儿多少钱? How much is this? |
mǎ shàng jiù dào. 马上就到。 (I) will be there any minute. wǒ mǎ shàng jiù dào. 我马上就到。 I will be there any minute. | mǎ ràng jiù dào. 马上就到。 (I) will be there any minute. wǒ mǎ ràng jiù dào. 我马上就到。 I will be there any minute. |
wǒ gào sù nǐ. 我告诉你。 I'm telling you. wǒ gào sù nǐ, zhèr diàn yǐngr lǎo hǎo kàn le. 我告诉你,这儿电影儿老好看了。 I'm telling you that this movie is amazing. | wǒ gào rù nǐ. 我告诉你。 I'm telling you. wǒ gào rù nǐ, zhèr diàn yǐngr lǎo hǎo kàn le. 我告诉你,这儿电影儿老好看了。 I'm telling you that this movie is amazing. |
BONUS: DOWNLOAD A SUMMARY (MP3 + PDF) BELOW THIS VIDEO
In fast speech… /j/, /q/, /x/ can change to /y/
Examples:
Standard Mandarin Chinese | Fast Northern Chinese Accent |
|---|---|
xī hóng shì chǎo jī dàn. 西红柿炒鸡蛋。 A dish of tomato fried eggs. lǎo bǎn, lái yī fènr xī hóng shì chǎo jī dàn. 老板,来一份儿西红柿炒鸡蛋。 Boss, get me a dish of tomato fried eggs. | xī hóng shì chǎo yī dàn. 西红柿炒鸡蛋。 A dish of tomato fried eggs. lǎo bǎn, lái yī fènr xī hóng shì chǎo yī dàn. 老板,来一份儿西红柿炒鸡蛋。 Boss, get me a dish of tomato fried eggs. |
gǎn jǐn qù. 赶紧去。 Hurry up! / Go quickly! | gǎn yǐn qù. 赶紧去。 Hurry up! / Go quickly! |
/w/ pronounced similar to an English /v/
Examples:
Standard Mandarin Chinese | Northern Chinese Accent |
|---|---|
wèn 问 To ask | vèn 问 To ask |
wén 闻 To smell | vén 闻 To smell |
nǐ xǐ huān mǎi dōng xī ma? wèi shén me? 你喜欢买东西吗?为什么? Do you like shopping? Why? | nǐ xǐ huān mǎi dōng xī ma? vèi shén me? 你喜欢买东西吗?为什么? Do you like shopping? Why? |
fā wēi xìn. 发微信。 Send messages on Wechat. | fā vēi xìn. 发微信。 Send messages on Wechat. |
tōng cháng hé péng yǒu chū qù wánr. 通常和朋友出去玩儿。 I usually go out and have fun with my friends. | tōng cháng hé péng yǒu chū qù vánr. 通常和朋友出去玩儿。 I usually go out and have fun with my friends. |
BONUS: DOWNLOAD A SUMMARY (MP3 + PDF) BELOW THIS VIDEO
/o/ pronounced similar to /e/
Examples:
Standard Mandarin Chinese | Northern Chinese Accent |
|---|---|
bó shì 博士 doctor / Ph.D. | bé shì 博士 doctor / Ph.D. |
nǐ men zhōu mò dǎ suàn zuò shén me? 你们周末打算做什么? What are you going to do this weekend? | nǐ men zhōu mè dǎ suàn zuò shén me? 你们周末打算做什么? What are you going to do this weekend? |
Extensive use of the "Neutral tone"
The second syllable in many two-syllable words changes to a "neutral tone" (e.g. wǎn shàng > wǎn shang).
Examples:
Without Neutral Tone | With Neutral Tone |
|---|---|
wǎn shàng 晚上 evening nǐ zuó tiān wǎn shàng zuò le shén me? 你昨天晚上做了什么? What did you do last night? | wǎn shang 晚上 evening nǐ zuó tiān wǎn shang zuò le shén me? 你昨天晚上做了什么? What did you do last night? |
BONUS: DOWNLOAD A SUMMARY (MP3 + PDF) BELOW THIS VIDEO
Tones change for emphasis
Examples:
Standard Mandarin Chinese | Northern Chinese Accent |
|---|---|
hái 还 still hái shuō huà! ān jìng! 还说话!安静! (You're) still talking. Be quiet! | hài 还 still hài shuō huà! ān jíng! 还说话!安静! (You're) still talking. Be quiet! |
bié 别 Don't bié shuō le! 别说了! Don't talk! / Stop talking! bié gēn wǒ tán liàn ài, zán men jié hūn ba! 别跟我谈恋爱,咱们结婚吧! Don't just date me, let's get married! | biè 别 Don't biè shuō le! 别说了! Don't talk! / Stop talking! biè gēn wǒ tán liàn ài, zán men jié hūn ba! 别跟我谈恋爱,咱们结婚吧! Don't just date me, let's get married! |
dé dào 得到 to get dé dào xìng fú. 得到幸福。 To get happiness. | dě dào 得到 to get dě dào xìng fú. 得到幸福。 To get happiness. |
hǎo xiē 好些 A lot hǎo xiē gè dú yīn dōu bù yī yàng. 好些个读音都不一样。 A lot of words are pronounced differently. | háo xiē 好些 A lot háo xiē gè dú yīn dōu bù yī yàng. 好些个读音都不一样。 A lot of words are pronounced differently. |
gěi wǒ chū qù! 给我出去! Get out! | gěi wǒ chù qu! 给我出去! Get out! or gěi wǒ chǔ qu! 给我出去! Get out! |
xí fur 媳妇儿 Wife wǒ xí fur shì běi jīng rén. 我媳妇儿是北京人。 My wife is Beijingnese. | xǐ fur 媳妇儿 Wife wǒ xǐ fur shì běi jīng rén. 我媳妇儿是北京人。 My wife is Beijingnese. |
On a computer: Right click on the button and select "Save as" or "Download"
On a phone: Tap and hold your finger on the button for a second (and you'll see the download option in the menu that pops up)
You might also find these posts interesting: